how to use brinell hardness test on harder materials|brinell hardness test example : agencies How to test the hardness of your material, using Brinell, Rockwell, Vickers or Leeb testing methods. quality free shemale porn tube and tranny sex videos. Watch HD and 4k Transsexual hardcore clips at sheshaft.com
{plog:ftitle_list}
Resultado da Watch Benfica Tv live tv stream. Watch Live sports events cricket, football, nfl, mlb, moto race and more sports games on Benfica Tv live channel free from livecric.
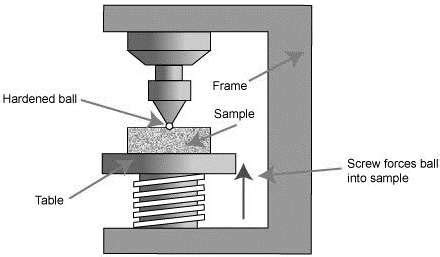
The Brinell hardness test is based on the amount of resistance that a solid material offers when it is pressed into by force. Brinell’s method produces a small depression .When measuring hardness using the Brinell method, a hardened steel or carbide ball of known diameter under a known load is forced into the material being tested. The diameter of the . In Brinell hardness testing, a hard metal ball (carbide ball) is pressed into the material surface to be tested within approximately 10 seconds as the force increases. The applied test force is maintained for 15 to 20 seconds .How to test the hardness of your material, using Brinell, Rockwell, Vickers or Leeb testing methods.
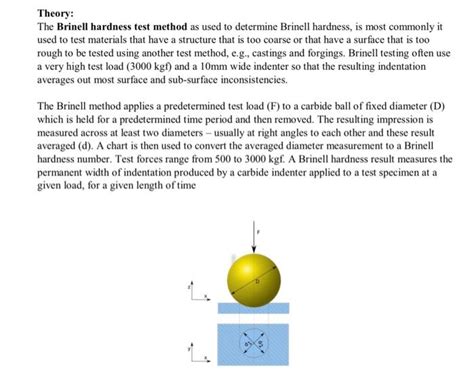
The Brinell hardness test method as used to determine Brinell hardness, is defined in ASTM E10. Most commonly it is used to test materials that have a structure that is too coarse or that have a surface that is too rough to be tested .The Brinell method can be used for testing non-homogeneous materials (e.g. castings), because the large ball comes into contact with many crystals (different metallographic .
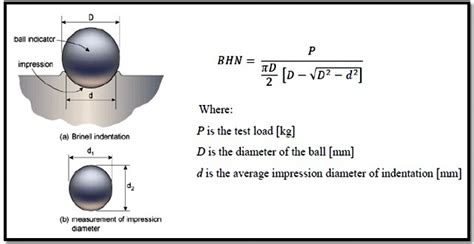
The Brinell hardness test consists of applying a constant load, usually in the range 500–3000 N, for a specified period of time (10–30 s) using a 5 or 10 mm diameter hardened steel or .For softer materials, a smaller force is used; for harder materials, a tungsten carbide ball is substituted for the steel ball. The indentation is measured and hardness calculated as: where: BHN = Brinell Hardness Number (kgf/mm 2) .
In the standard method of the Brinell Hardness Test, we use 250 to 500 kg of load for soft material and 500 to 3000 kg of load for hard material such as steel and iron. In the standard method of the test, we use a ball . The Brinell hardness number (BHN or HBW) describes the hardness of a material. The higher the number, the harder the material. The Brinell hardness test involves pressing a small metal ball into the surface of the test material with a known amount of force. The resulting indentation is then measured and converted into a hardness number.Learrn more about hardness testing basics here. The Brinell hardness test method as used to determine Brinell hardness, is defined in ASTM E10. Most commonly it is used to test materials that have a structure that is too coarse .
How to test the hardness of your material, using Brinell, Rockwell, Vickers or Leeb testing methods. Real Talk . Hard anodised parts are tested for hardness using the Vickers test. On average, hard anodised aluminium 6082 can achieve values in the range of 300 to 500 HV, to put that into perspective, in its untreated state it has a hardness .The Brinell hardness test is a standardized test used for measuring the hardness of metals and other hard materials. It is performed by measuring penetration depth into a standardized material with a known hardness, typically steel or copper, when an object with a known force is pressed into it at a standard rate. Brinell Hardness Test. Involves pressing a hard steel or carbide ball into the material and measuring the diameter of the indentation. Pros: Good for testing materials with coarse or uneven grain structures. Cons: Not suitable for very hard or thin materials. Industrial Use: Widely used in the metal industry, particularly for softer metals.
The Brinell hardness test. The Brinell hardness test is used for hardness testing larger samples in materials with a coarse or inhomogeneous grain structure. The Brinell hardness test (HBW) indentation leaves a relatively large impression, using a tungsten carbide ball. The size of the indent is read optically.The Brinell hardness test is particularly useful for materials with a coarse microstructure or those too rough or thick to be accurately measured using other methods. One of the most popular instruments used for Brinell hardness testing is the King Brinell hardness tester, which is known for its accuracy and reliability.
He wanted to find a method to control the quality/hardness of steel. His solution was to press a railway wheel-bearing ball into the material and then measure the size of the mark it left. The method proved reliable and in 1900 the Brinell hardness test was officially born. Today, the Brinell test is performed using a Brinell hardness test unit.
Brinell hardness test is one of indentation hardness tests, that has been developed for hardness testing. In Brinell tests, a hard, spherical indenter is forced under a specific load into the surface of the metal to be tested. . For softer materials, a smaller force is used; for harder materials, a tungsten carbide ball is substituted for the .Though loads of 500, 1000, 1500, 2000, 2500, and 3000 N are available in a typical Brinell hardness tester, a load of 500 N is used for testing relatively soft metals such as copper and aluminium alloys, while the 3000 N load is often used for testing harder materials such as steels and cast irons.However, the general rule is that the combination of test load and ball diameter . A numerical hardness value is assigned to the test material based on the results of the test. Mohs hardness test uses 10 reference materials of varying hardness as the scale for the test. The softest material used is talc (value=1) and the hardest material is .
brinell hardness tester diagram
Though loads of 500, 1000, 1500, 2000, 2500, and 3000 N are available in a typical Brinell hardness tester, a load of 500 N is used for testing relatively soft metals such as copper and aluminium alloys, while the 3000 N load is often used for testing harder materials such as steels and cast irons.However, the general rule is that the combination of test load and ball diameter .
The Brinell hardness test measures material hardness by determining the diameter of an indentation made by a hardened steel or carbide ball under a specific load. A load, typically ranging from 500 to 3,000 kgf, is applied to the material’s surface for 10-15 seconds, allowing the ball to penetrate and create an indentation. . For materials .Rockwell B scale (RHB): This scale is used for testing harder materials, such as brass, mild steel, and annealed copper alloys. The load applied is 100 kgf and the diamond cone indenter is used. . Another difference is the amount of .The Vickers hardness test method was developed by Robert L. Smith and George E. Sandland at Vickers Ltd as an alternative to the Brinell method to measure the hardness of materials. The Vickers hardness test method can .
When is the Brinell hardness test used? Brinell hardness testing is a commonly used method for determining the hardness of metals and alloys. The Brinell hardness test formula. When measuring hardness using the Brinell method, a hardened steel or carbide ball of known diameter under a known load is forced into the material being tested.
The Vickers hardness test method was developed by Robert L. Smith and George E. Sandland at Vickers Ltd as an alternative to the Brinell method to measure the hardness of materials. The Vickers hardness test method can be also used as a microhardness test method, which is mostly used for small parts, thin sections, or case depth work. Since the . The HRB scale typically is used for soft materials such as aluminum and brass alloys. It uses a 1/16-in. ball indenter with a 100-KG test force. Brinell Testing. Brinell testing normally is used for larger, heavy-walled pipe. Because the Brinell test is not a depth-measuring technique, it is more forgiving. Brinell Hardness Test. The Brinell hardness test entails measuring the diameter of indentation caused by a constant concentrated force applied by a steel or carbide spherical indenter on a test specimen. The steel ball indenter is first placed in contact with the material before a constant force is applied and maintained for a 10 to 15 second duration, . Variants on the Rockwell hardness test procedure are used depending on the material and strength of a part. The most common Rockwell variants include: HRC – Known as “Rockwell C,” a 150 kgf load is applied via a diamond in this method.
In materials science, hardness (antonym: softness) is a measure of the resistance to localized plastic deformation, such as an indentation (over an area) or a scratch (linear), induced mechanically either by pressing or abrasion.In general, different materials differ in their hardness; for example hard metals such as titanium and beryllium are harder than soft . This is mainly because harder materials are usually more fragile and offer less energy absorption before they break. For example, hard high-carbon steel has lower ductility than the soft low-carbon steel. . hardness by measuring the diameter of the resulting indentations using a carbide ball or hardened steel is known as Brinell hardness test .
A Rockwell hardness tester. The Rockwell scale is a hardness scale based on indentation hardness of a material. The Rockwell test measures the depth of penetration of an indenter under a large load (major load) compared to the penetration made by a preload (minor load). [1] There are different scales, denoted by a single letter, that use different loads or indenters.
The unit of measurement for Brinell hardness is the Brinell hardness number (BHN). A higher BHN value indicates a harder material, while a lower value signifies a softer one. . In the manufacturing industry, the Brinell Hardness Test is used to assess the hardness of raw materials, such as metals and alloys, before processing and fabrication. . Related reading: Metal Hardness Comparison Chart: HV, HB, HRC Commonly Used Hardness Brinell Hardness. The Brinell hardness test uses a ball made of hardened steel or a hard alloy with a diameter of D as the indenter.. A specified test force F is applied to the surface of the material being tested, and after a designated hold time, the test force is .
brinell hardness test theory
The Brinell hardness test is used to determine hardness and is done by forcing a hard steel or carbide ball indenter of a specified diameter onto the test metal surface under a specified load. This is followed by measuring the diameter of .
webSearch the world's information, including webpages, images, videos and more. Google has many special features to help you find exactly what you're looking for.
how to use brinell hardness test on harder materials|brinell hardness test example